Patient Toolkit
Patient Toolkit
The Fabry disease glossary
When you read about Fabry disease, you may find there are difficult medical words that are difficult to understand. In this glossary, you will find a list of medical words related to Fabry disease and what they mean.
If you would like a printed version of this list, you can print it by clicking the printer button below this document.
Acroparesthesia
ak-roh-par-uhs-thee-zhuh
Aburning, tingling, or pricking sensation or numbness in the hands or feet. A common symptom in people with Fabry disease.1,2
Alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-GAL)
al-fuh-gal-ac-toos-i-deys A
An enzyme (protein) that removes a type of fat called globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) inside the body.3 In people with Fabry disease, this enzyme is missing or does not work well, leading to a build-up of this fat in blood vessels and organs.2,4
Anhidrosis
an-hi-droh-sis
Not being able to sweat. A common symptom in people with Fabry disease, more often in boys and men.5
Angiokeratomas
an-jee-oh-ker-uh-toh-muhz
Small, red or dark-blue spots on the skin. The most common skin symptom in people with Fabry disease.5
Arrhythmia
uh-rith-mee-uh
Having an irregular heartbeat.6 A common symptom in people with Fabry disease.7
Cardiologist
kahr-dee-ol-uh-jist
A doctor who specialises in the heart and heart conditions, including the diagnosis, management and treatment of them.8
Chaperone therapy
shap-uh-rohnther-uh-pee
A medication for people with Fabry disease that helps correct faults in the enzyme, alpha-Gal, so that it can break down extra fat (Gb3).9
Chronic kidney disease
kron-ikkid-nee dih-zeez
A condition where the kidneys are damaged and can’t filter blood as good as they should.10
Corneal opacity
kawr-nee-uhloh-pas-i-tee
A condition where a hazy cream-coloured circle develops on the cornea (the transparent part of the eyeball that covers the iris and pupil and lets light in).11,12 This usually happens when the cornea has been damaged and can lead to a loss of vision.13 However, it does not usually affect the vision of people with Fabry disease.7
Enzyme
en-zahym
A complex protein that is produced by living cells and is reponsible for speeding up certain chemical reactions in our body. Without enzymes, most metabolic reactions would take much longer and would not be fast enough to sustain life.14
Enzyme assay
en-zahymas-ey
A test that measures the activity of a particular enzyme.15 An assay for alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal) is used to check whether a person has Fabry disease. In boys and men, low activity of alpha-Gal means they have Fabry disease. In girls and women, a genetic test is done to check for Fabry disease. This is because girls and women with Fabry disease may have normal alpha-Gal activity.5
Enzyme replacement therapy
en-zahymri-pleys-muhnt ther-uh-pee
A medication that provides new healthy enzymes to a person that is missing that enzyme or whose enzymes do not work well.16 Enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease contains the enzyme alpha-Gal.5
GalactosidaseAlpha (GLA) gene mutation
guh-lak-toh-si-deys
al-fuh myoo-tey-shuhn
A gene mutation is a permanent change in the structure of a gene that may change how it works.17
The GLA gene makes possible the production of an enzyme called alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal).7 A mutation in the GLA gene means that it has changed and may not work as it should. People with Fabry disease have a GLA gene mutation.2
Gastrointestinal symptom
gas-troh-in-tes-tuh-nlsimp-tuhm
Any symptom that happens in your gastrointestinal system, from your mouth to your stomach and intestines.18 Examples of gastrointestinal symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, flatulence, a feeling of fullness earlier than normal, nausea and vomiting.19,20 Gastrointestinal symptoms are common in people with Fabry disease.19
Genetic counselor
juh-net-ik koun-suh-ler
A healthcare professional who provides information to patients and families about heritable disease.21,22
Genotype
jee-noh-taip
The set of genes that each person, animal or organism has.23
Globotriaosylceramide (Gb3)
gloh-boh-trahy-uh-oh-ser-ahm-ahyd
A type of fat in cells of the body that helps cells divide and communicate.3 To keep a healthy level of this fat, the body sends an enzyme called alpha-GAL to remove this fat.3 However, in people with Fabry disease, alpha-GAL is missing or does not work as well, so this fat builds up in the body.2
Glycosphingolipid
glahy-kuh-sfing-guh-lip-id
A type of fat inside the cells of the body that helps cells divide and communicate. Globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) is an example of a glycosphingolipid.3 Gb3 is the type of fat that builds up in the cells and organs in people with Fabry disease.2
Heterozygote
heh-tuh-row-zai-got
A person, animal, or organism that has two different forms of a gene (part of a cell that contains DNA information).24,25
Hypohidrosis
hi-poh-hi-droh-sis
Sweating less than normal. A symptom that people with Fabry disease may experience, more common in boys and men.5
Ischemic stroke
ih-skee-mik strohk
A condition where the blood flow to the brain is blocked. An ischemic stroke is a medical emergency and needs immediate medical attention.26
Left ventricular hypertrophy
left ven-trik-yuh-ler hahy-pur-truh-fee
A condition where the left ventricle (cavity) of the heart grows bigger, or the wall grows thicker, than it should.27 Heart conditions, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, are common in people with Fabry disease.7
Lyso Gb3 (globotriaosylsphingosine)
gloh-boh-trahy-uh-oh-sil-sfing-goh-seen
A different form of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3), a type of fat that builds up in people with Fabry disease.5 Lyso Gb3 is thought to play a role in Fabry disease because it speeds up the storage of Gb3.28
Lysosomal storage disorder
lahy-suh-soh-muhl
tohr-ij dis-awr-der
A genetic condition where a person is missing an enzyme (protein), which leads to an abnormal build-up of certain substances in the body. Seventy lyosomal storage disorders have been discovered, and more are likely to be discovered in the future. Fabry disease is a lysosomal storage disorder.29
Medical geneticist
med-i-kuhl juh-net-uh-sist
A doctor who specialises in genetic conditions and how to manage and treat them. They can also provide counseling to patients with genetic conditions.30
Multidisciplinary team
muhl-tee-dis-uh-pluh-ner-ee teem
A group of healthcare professionals, such as a cardiologist, medical geneticist, nephrologist, neurologist, psychologist, from multiple areas of expertise that works together on a patient’s care and treatment.31
Nephrologist
neh-frah-leh-jist
A doctor who specialises in kidneys and kidney conditions.32 Your kidneys are organs that filter your blood and remove waste and extra water.33
Nervous system
nur-vuhs sis-tuhm
The network of nerves and cells that carry the signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It enables thinking, language, feeling, learning, memory. The nervous system has 2 parts:34
1. The central nervous system: this is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system: the network of nerves that extend throughout the body.35
Neurologist
noo-rol-uh-jist
A doctor who specialises in brain and nerves and how to treat conditions that affect them.36
Neuropathic pain
noo-rop-uh-thick peyn
A pain that is caused when parts of the nervous system to do with the touch sensation are damaged.37 A very common symptom in people with Fabry disease that is probably caused by a build-up of certain fats in the nerves.38
Phenotype
Phee-noh-taip
The physical characteristics of something living that can be seen.39
Psychologist
sahy-kol-uh-jist
A trained healthcare professional who uses talking therapies to treat mental health problems and help people cope with emotional, social and physical problems.40 If you need support to help cope with your Fabry diagnosis or symptoms, your doctor may refer you to a psychologist.
Tinnitus
tin-i-tuhs
Hearing noises that do not come from an outside source. They can sound like ringing, hissing, whistling, humming, buzzing, chirping, or clicking sounds.41 In people with Fabry disease, doctors think tinnitus is caused by blocking or narrowing of the blood vessels in the inner ear caused by a build-up of Gb3.42
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
tran-zee-uhnt ich-skee-mik uh-tak
A condition where the blood flow to the brain is blocked for a short period of time (usually less than 5 minutes).43 This type of stroke is also known as a ‘mini-stroke’.44 A TIA is a medical emergency and needs immediate medical attention.43
ak-roh-par-uhs-thee-zhuh
Aburning, tingling, or pricking sensation or numbness in the hands or feet. A common symptom in people with Fabry disease.1,2
al-fuh-gal-ac-toos-i-deys A
An enzyme (protein) that removes a type of fat called globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) inside the body.3 In people with Fabry disease, this enzyme is missing or does not work well, leading to a build-up of this fat in blood vessels and organs.2,4
an-hi-droh-sis
Not being able to sweat. A common symptom in people with Fabry disease, more often in boys and men.5
an-jee-oh-ker-uh-toh-muhz
Small, red or dark-blue spots on the skin. The most common skin symptom in people with Fabry disease.5
uh-rith-mee-uh
Having an irregular heartbeat.6 A common symptom in people with Fabry disease.7
kahr-dee-ol-uh-jist
A doctor who specialises in the heart and heart conditions, including the diagnosis, management and treatment of them.8
shap-uh-rohnther-uh-pee
A medication for people with Fabry disease that helps correct faults in the enzyme, alpha-Gal, so that it can break down extra fat (Gb3).9
kron-ikkid-nee dih-zeez
A condition where the kidneys are damaged and can’t filter blood as good as they should.10
kawr-nee-uhloh-pas-i-tee
A condition where a hazy cream-coloured circle develops on the cornea (the transparent part of the eyeball that covers the iris and pupil and lets light in).11,12 This usually happens when the cornea has been damaged and can lead to a loss of vision.13 However, it does not usually affect the vision of people with Fabry disease.7
en-zahym
A complex protein that is produced by living cells and is reponsible for speeding up certain chemical reactions in our body. Without enzymes, most metabolic reactions would take much longer and would not be fast enough to sustain life.14
en-zahymas-ey
A test that measures the activity of a particular enzyme.15 An assay for alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal) is used to check whether a person has Fabry disease. In boys and men, low activity of alpha-Gal means they have Fabry disease. In girls and women, a genetic test is done to check for Fabry disease. This is because girls and women with Fabry disease may have normal alpha-Gal activity.5
en-zahymri-pleys-muhnt ther-uh-pee
A medication that provides new healthy enzymes to a person that is missing that enzyme or whose enzymes do not work well.16 Enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease contains the enzyme alpha-Gal.5
guh-lak-toh-si-deys
al-fuh myoo-tey-shuhn
A gene mutation is a permanent change in the structure of a gene that may change how it works.17
The GLA gene makes possible the production of an enzyme called alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal).7 A mutation in the GLA gene means that it has changed and may not work as it should. People with Fabry disease have a GLA gene mutation.2
gas-troh-in-tes-tuh-nlsimp-tuhm
Any symptom that happens in your gastrointestinal system, from your mouth to your stomach and intestines.18 Examples of gastrointestinal symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, flatulence, a feeling of fullness earlier than normal, nausea and vomiting.19,20 Gastrointestinal symptoms are common in people with Fabry disease.19
juh-net-ik koun-suh-ler
A healthcare professional who provides information to patients and families about heritable disease.21,22
jee-noh-taip
The set of genes that each person, animal or organism has.23
gloh-boh-trahy-uh-oh-ser-ahm-ahyd
A type of fat in cells of the body that helps cells divide and communicate.3 To keep a healthy level of this fat, the body sends an enzyme called alpha-GAL to remove this fat.3 However, in people with Fabry disease, alpha-GAL is missing or does not work as well, so this fat builds up in the body.2
glahy-kuh-sfing-guh-lip-id
A type of fat inside the cells of the body that helps cells divide and communicate. Globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) is an example of a glycosphingolipid.3 Gb3 is the type of fat that builds up in the cells and organs in people with Fabry disease.2
heh-tuh-row-zai-got
A person, animal, or organism that has two different forms of a gene (part of a cell that contains DNA information).24,25
hi-poh-hi-droh-sis
Sweating less than normal. A symptom that people with Fabry disease may experience, more common in boys and men.5
ih-skee-mik strohk
A condition where the blood flow to the brain is blocked. An ischemic stroke is a medical emergency and needs immediate medical attention.26
left ven-trik-yuh-ler hahy-pur-truh-fee
A condition where the left ventricle (cavity) of the heart grows bigger, or the wall grows thicker, than it should.27 Heart conditions, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, are common in people with Fabry disease.7
gloh-boh-trahy-uh-oh-sil-sfing-goh-seen
A different form of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3), a type of fat that builds up in people with Fabry disease.5 Lyso Gb3 is thought to play a role in Fabry disease because it speeds up the storage of Gb3.28
lahy-suh-soh-muhl
tohr-ij dis-awr-der
A genetic condition where a person is missing an enzyme (protein), which leads to an abnormal build-up of certain substances in the body. Seventy lyosomal storage disorders have been discovered, and more are likely to be discovered in the future. Fabry disease is a lysosomal storage disorder.29
med-i-kuhl juh-net-uh-sist
A doctor who specialises in genetic conditions and how to manage and treat them. They can also provide counseling to patients with genetic conditions.30
muhl-tee-dis-uh-pluh-ner-ee teem
A group of healthcare professionals, such as a cardiologist, medical geneticist, nephrologist, neurologist, psychologist, from multiple areas of expertise that works together on a patient’s care and treatment.31
neh-frah-leh-jist
A doctor who specialises in kidneys and kidney conditions.32 Your kidneys are organs that filter your blood and remove waste and extra water.33
nur-vuhs sis-tuhm
The network of nerves and cells that carry the signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It enables thinking, language, feeling, learning, memory. The nervous system has 2 parts:34
1. The central nervous system: this is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
2. The peripheral nervous system: the network of nerves that extend throughout the body.35
noo-rol-uh-jist
A doctor who specialises in brain and nerves and how to treat conditions that affect them.36
noo-rop-uh-thick peyn
A pain that is caused when parts of the nervous system to do with the touch sensation are damaged.37 A very common symptom in people with Fabry disease that is probably caused by a build-up of certain fats in the nerves.38
Phee-noh-taip
The physical characteristics of something living that can be seen.39
sahy-kol-uh-jist
A trained healthcare professional who uses talking therapies to treat mental health problems and help people cope with emotional, social and physical problems.40 If you need support to help cope with your Fabry diagnosis or symptoms, your doctor may refer you to a psychologist.
tin-i-tuhs
Hearing noises that do not come from an outside source. They can sound like ringing, hissing, whistling, humming, buzzing, chirping, or clicking sounds.41 In people with Fabry disease, doctors think tinnitus is caused by blocking or narrowing of the blood vessels in the inner ear caused by a build-up of Gb3.42
tran-zee-uhnt ich-skee-mik uh-tak
A condition where the blood flow to the brain is blocked for a short period of time (usually less than 5 minutes).43 This type of stroke is also known as a ‘mini-stroke’.44 A TIA is a medical emergency and needs immediate medical attention.43
References:
- Slouma M, et al. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2024;20(2):115-126.
- Ellaway C. Paediatric Fabry disease. Transl Pediatr. 2016;5(1):37-42.
- Celi AB, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2022:9;813637.
- Hamed A, et al. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021;29:100824.
- Ezgu F, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17(1):90.
- Kingma J, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(6):844.
- Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010;5:30.
- Mishra S. Indian Heart J. 2015;67(6):509-511.
- Nowicki M, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 19(1):16.
- Chen TK, et al. JAMA. 2019;322(13):1294-1304.
- Gambini G, et al. J Pers Med. 2023 May 27;13(6):904.
- ‘Cornea’, Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/cornea. Accessed July 2025.
- Wilson SE, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63(1):22.
- Lewis T, Stone WL. Biochemistry, Proteins Enzymes. [Updated 2023 Apr 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554481/. Accessed July 2025.
- Ciuffreda P, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(14):7693.
- de la Fuente M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9181.
- Durland J, Ahmadian-Moghadam H. Genetics, Mutagenesis. [Updated 2022 Sep 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560519/. Accessed July 2025.
- Ogobuiro I, Gonzales J, Shumway KR, et al. Physiology, Gastrointestinal. [Updated 2023 Apr 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537103/#. Accessed July 2025.
- Zar-Kessler C, et al. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9(4):626-634.
- Lenders M, et al. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2022;8(3):272-281.
- Biesecker B. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020;10(3):a038968.
- Yeates L, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020;28(9):1137-1138.
- Mahner M, Kary M. J Theor Biol. 1997;186(1):55-63.
- ‘Heterozygote’, Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/heterozygote. Accessed July 2025.
- ‘Heterozygous’, Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/heterozygous. Accessed July 2025.
- Kuriakose D, Xiao Z. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7609.
- Bornstein AB, et al. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. [Updated 2023 Apr 30]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557534. Accessed July 2025.
- Choi L, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2015;594:163-168.
- Rajkumar V, Dumpa V. Lysosomal Storage Disease. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563270. Accessed July 2025.
- Epstein CJ. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;79(3):434-438.
- Paim-Marques L, et al. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022;15:485-495.
- Maxwell AP. Ulster Med J. 2010;79(3):154-155.
- Ogobuiro I, Tuma F. Physiology, Renal. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538339/. Accessed July 2025.
- Ludwig PE, Reddy V, Varacallo M. Neuroanatomy, Central Nervous System (CNS) [Updated 2022 Oct 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442010/. Accessed July 2025.
- Bazira PJ. Surgery (Oxford). 2021;39(8):451-462.
- Engstrom JW, Hauser SL. West J Med. 1994;161(3):331-334.
- Finnerup NB, et al. Physiol Rev. 2021;101(1):259-301.
- Burlina AP, et al. BMC Neurol. 2011;11:61.
- Orgogozo V, et al. Front Genet. 2015;6:179.
- Wahass SH. J Family Community Med. 2005;12(2):63-70.
- Wu V, et al. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64(7):491-495.
- Cheng YF, et al. J Clin Med. 2022;11(24):7396.
- Amarenco P. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1933-1941.
- Mc Sharry J, et al. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104434.
Rethink Fabry™ is a trademark of CHIESI FARMACEUTICI S.p.A.
Date of preparation: July 2025
ALL_25_99
Daily Symptoms Tracker
The Daily Symptoms Tracker can help you keep track of your symptoms and record any changes to discuss with your doctor.
Patient support groups
International and local patient organisations can help you learn more about living with Fabry disease and connect with others sharing a similar experience.
Links to our channels
To find out more about Chiesi GRD, please visit our website or follow us on social media.
Reference
- Ortiz 2018 416-427
- fabrydiseasenews.com-What Is Fabry Disease
- fabrydiseasenews.com-Fabry Disease and the Heart
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Fabry disease is a rare genetic condition. About 1 in 22,000-40,000 males are affected with the classic type of Fabry disease. About 1 in 1,000–3,000 males and 1 in 6,000–40,000 females are affected with the late-onset/atypical type of Fabry disease.1
In people with Fabry disease, an enzyme (protein; alpha-galactosidase A) that removes a type of fat is missing or does not work well.2 This leads to a build-up of these fats in blood vessels and organs which can lead to a range of manifestations.3,4
Some of the most common symptoms of Fabry disease are:3,5
- Severe pain episodes
- Burning and tingling sensations in the hands and feet
- Small, red or dark-blue spots on the skin
- Sweating abnormalities. Sweating less than is usual or not at all
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Hazy eyes (corneal opacity)
- Hearing problems
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Heart problems
- Kidney problems
- Nervous system problems
The symptoms and the severity can vary greatly between people with Fabry disease. A person with Fabry disease may not have all of these symptoms, but may only have a few.6
You may or you may not have the same symptoms as a family member with Fabry disease. The symptoms and the severity of the symptoms can vary greatly between people with Fabry disease.6
Yes, Fabry disease may affect men and women differently. Although it can differ per person, generally, men are more severely affected by Fabry disease.5
For a long time it was thought that women were only carriers of the disease and that they did not have any symptoms. However, we now know that this is not the case.7 Many women with Fabry disease do have symptoms, however, symptoms may vary more and certain symptoms may be milder or absent in women.7,8
Men may have more severe symptoms and have Fabry disease that gets worse more quickly over time.5
Fabry disease is a genetic condition and therefore a person is born with Fabry disease. Depending on the type of Fabry disease, symptoms may appear in childhood/adolescence (classic type) or at an older age in adulthood (late-onset/atypical type).5
No, Fabry disease is not contagious, it is an inherited disease. You can only get Fabry disease if one or both of your parents has it.9,10
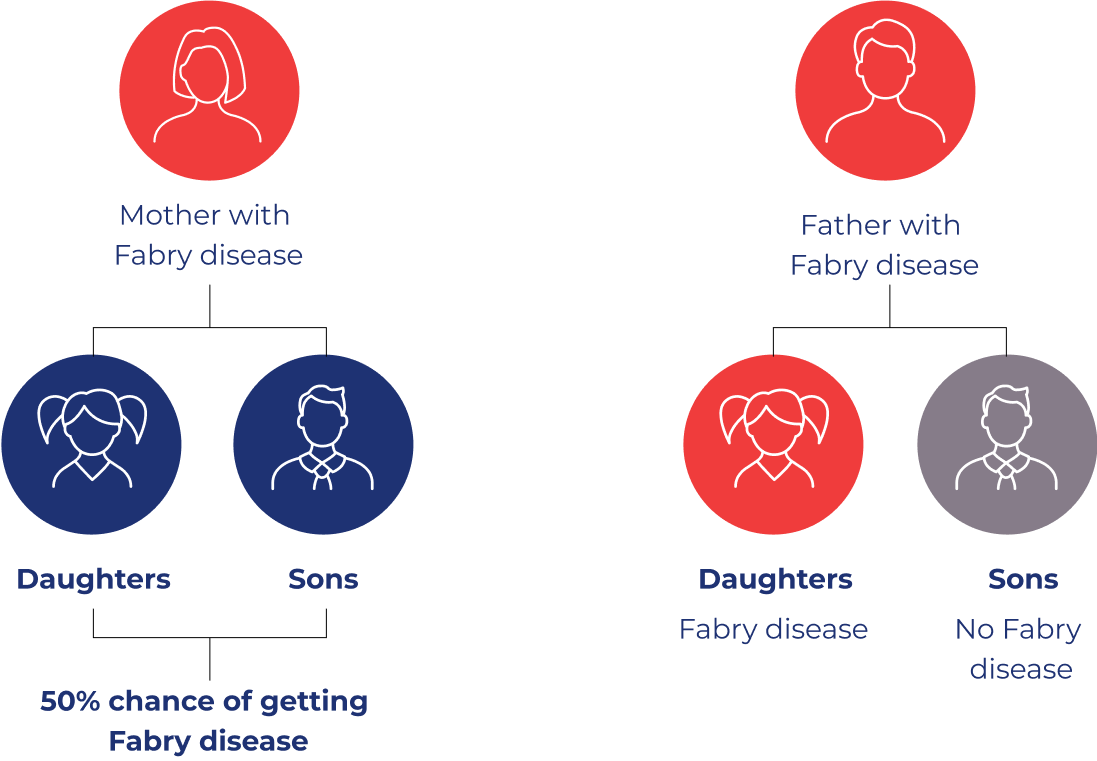
Fabry disease is a inherited disease. This means it is passed on through genes from your parents. Mothers with Fabry disease have a 50% chance of passing the Fabry gene on to their children. Fathers with Fabry disease pass on the Fabry gene to none of their sons and all of their daughters.9,10
How Fabry is passed on from mothers and fathers10
If you and/or your doctor suspect you may have Fabry disease, your doctor will do a blood test. In boys/men, the doctor will check the level of alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A).5 Alpha-Gal A is the enzyme that is missing or does not work well in people with Fabry disease.3 In girls/women, the doctor will also check for certain genes. This is because girls and women with Fabry disease may have normal alpha-Gal A activity.5
How long a person with Fabry disease lives will vary and depend on certain factors. For example, which genes mutation you have, the age at which Fabry disease symptoms started, when you were diagnosed and started treatment.5,11 These factors can affect if, and how fast, your Fabry disease will get worse.5
On average, people with Fabry disease do not live as long as people without Fabry disease. Data from 2848 patients in the Fabry Registry (including both treated and untreated patients) showed that men with Fabry disease on average lived to about 58 years compared to 75 years for men in the general population. Women with Fabry disease on average lived to about 75 years compared to 80 years for women in the general population.12
However, life expectancy of people with Fabry Disease is expected to improve in the future. New studies will help us understand Fabry disease better, and may lead to diagnosing and treating people with Fabry disease earlier. Earlier diagnosis and initiation of treatment would be expected to extend life expectancy.12
Yes, people with Fabry disease can have children. A study performed in 2005 has shown that fertility rates in both men and women with Fabry disease are usually normal.13 However, women with Fabry diseaese do have a higher risk of complications during pregnancy.14
If you or your partner have been diagnosed with Fabry disease and are thinking about having children, talk to your doctor. Your doctor will be able to refer you to a genetic counselor, which can help you understand the likelihood that your children will inherit Fabry disease.9,15
Currently, there are two types of treatments that have been approved for Fabry disease:16
- Enzyme replacement therapy
- Chaperone therapy
Your doctor will discuss which treatment option will be most suitable for you.
Enzyme replacement therapy works by providing new healthy enzymes to a person that is missing that enzyme or whose enzymes do not work well.18 Enzyme replacement therapy for Fabry disease contains the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A.5
In people with Fabry disease, this is the enzyme that or does not work well.3 Enzyme replacement therapy is given as an intravenous (into a vein) injection.5
Chaperone therapy works by stabilizing and correcting faults (misfolds) in the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A.5 This protein is mutated in people with Fabry disease, so it does not work well.3 The stabilized and corrected alpha-galactosidase A can then break down the fat (globotriaosylceramide or Gb3).5
Chaperone therapy only works in patients who have specific types of mutations in the enzymes and it is taken as a pill by mouth.5
Disclaimer: Rethink Fabry is not a substitute for instructions or advice from your doctor. Always discuss any questions or concerns about medical conditions with your doctor or health care professional.
Reference:
- Bokhari SRA, Zulfiqar H, Hariz A. Fabry Disease. [Updated 2023 Jul 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435996/. Accessed July 2025.
- Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010;5:30.
- Ellaway C. Paediatric Fabry disease. Transl Pediatr. 2016;5(1):37-42.
- Hamed A, et al. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021;29:100824.
- Ezgu F, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17(1):90.
- Dutra-Clarke M, et al. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2020;26:1007
- Wang RY, et al. Genet Med. 2007;9(1):34-45.
- Burand AJ, Stucky CL. Pain. 2021;162:1305-1321.
- Martins AM, et al. J Pediatr. 2009;155(4 Suppl):S19-S31.
- Izhar R, et al. Genes (Basel). 2024;15(1):37.
- Klingelhöfer D, et al. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020;8(9):e1163.
- Waldek S, et al. Genet Med. 2009:11(11):790-796.
- Hauser AC et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59(9):1025-1028.
- Haninger-Vacariu N, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024;19(1):165.
- Ortiz A, et al. Mol Genet Metab. 2018;123(4):416-427.
- Yoo H. J Genet Med. 2023;20(1):6-14.
- de la Fuente M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9181.
ALL_25_913
Patients & Caregivers: In case of need to report an adverse drug reaction, please refer to your physician, asking him to fill in and submit the relevant case report to the concerned Health Authority, according to the Pharmacovigilance requirements in force in your Country. Nevertheless, please be kindly reminded that each patient can report any such cases directly to the national reporting system.
Healthcare Professionals: in case you want to report an adverse drug reaction you become aware of, please report it to your Health Authority according to the requirements set by the pharmacovigilance legislation.
You are now leaving Rethink Fabry. Please note that the site you are entering is not the property of nor managed by Chiesi.